Code Tables
Core Concept
About Code Tables
Code tables are lists of codes, descriptions, and sometimes parameters. The name “code table” is traditional; codes are stored on the IFS Field Service Management (FSM) database but by default you see descriptions in the FSM interface. You can choose to see the codes instead.
At a minimum, a code table is a list of values you can select, for example, on a drop‐down list. The value might be display only, or you might be using it as a business rule parameter.
Other code tables have parameters associated with the value. The parameters affect how information associated with the value is used by FSM.
When you change a code table, you must refresh the cache to activate your changes.
Code Table Types
FSM Code Tables
FSM code tables cannot be changed by you. We determine the values and each value controls specific behavior known as policy, which is programmed into FSM. An example of an FSM code that controls policy is the day code, which specifies the day of the week.
Code Tables
Code tables contain values supplied by us and you can also add values that apply to your business processes. Each code has a set of parameters that control certain processing behaviors. For example, line codes determine quantity format and unit of measure, among other parameters. You can set the parameters of any code on code tables.
The application parameter CODES_USER_DEFS_TO_DISPLAY determines the number of user‐defined fields to display on the Code Tables screen. You can use these user‐defined fields to create custom parameters that can then be referenced by business rules.
Field Label |
Description |
| Access Group |
Identifies who can view and select this code value. |
| Active |
Indicates whether the code is active for selection. |
| Message ID |
Identifies the message to display as a description instead of the code value on drop‐down lists and reports. If a message ID is specified along with a 28 Core Concepts IFS description, the message appears instead of the description. Using a message enables a code description to be displayed in a local language. |
| Description |
Identifies the description to display instead of the code value. Does not appear when a message is specified. |
| Sequence |
When specified, identifies the order in which the code appears in the list. Codes without a sequence appear at the bottom. |
Global Code Tables
Global code tables are used to create a list of values for drop‐down list fields on the FSM interface. These fields generally do not affect policy but are used as informational‐only or can be used as parameters to business rules. There are no parameters associated with global codes. If you want to control the behavior of FSM using global codes, you set up business rules that use global codes as parameters.
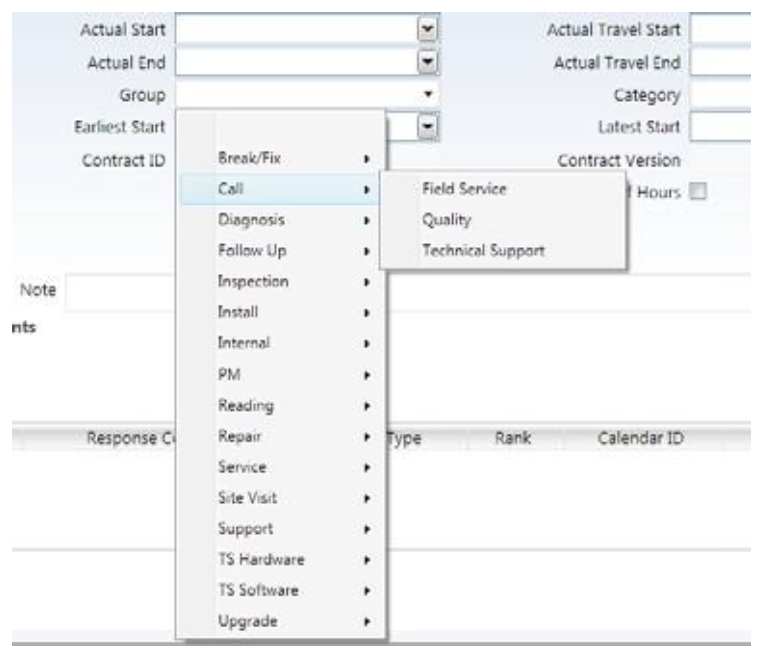
You can create a hierarchical structure for values defined on the Global Code table when selecting values on a list.
When you set up a hierarchical code structure, the lowest level of the hierarchy, on a screen, becomes a hierarchical menu. In other words, the hierarchy is built from the bottom up.
For example, suppose you set up global codes and descriptions for task group. Then, you specify a parent code and value for each task group code and description. You can, for example, specify task type as a parent. When a user selects the task group list, a list of task types appears with the task groups related to each task type.
Field Label |
Description |
| Code Name |
Identifies the code. |
| Parent Code Name |
For codes that are part of a hierarchy, identifies the code under which this code and a set of values appears. |
| Code Value |
Identifies a code value. |
| Sequence |
Identifies the order in which the code value appears on drop‐down lists. |
| Description |
Identifies the description to display instead of the code value. Does not appear when a message is specified. |
| Message ID |
Identifies the message to display as a description instead of the code value on drop‐down lists and reports. If a message ID is specified along with a description, the message appears instead of the description. Using a message enables a code description to be displayed in a local language. |
| Active |
Indicates whether the code value is available for selection. |
| Access Group |
Identifies who can view and select this code value. |
| Parent Code Value |
For codes that are part of a hierarchy, identifies the code value under which selected values above appear. |