Returns
Core Process
About Returns
The return process is used to authorize, receive, and ship items, usually for repair. Sometimes you use the return process to receive a returned part to put back into stock or to ship a part that you have sold.
Returns are authorized and tracked using a special type of request called a return material authorization (RMA).
Returns Process Description
Authorization
Authorization includes identifying the units to be returned. A unit is any single piece to be returned that you can identify with a serial number or asset number. Unless the unit is a part being returned to stock or sold to a customer, the unit is generally identified in IFS Field Service Management (FSM) using a Product record, which also means you can track its repair history.
Units to be returned are listed on the RMA as request lines. Each line has one or more of the same kind of unit, whether model or part. The quantity to be returned is specified on the line and when the units have serial numbers, the serial IDs are recorded for each line.
While you can enter serial numbers at authorization, we recommend that you enter them during receipt.
Units can be listed on only one open RMA at a time.
Types of Returns
Returns are classified on a request line by return type. The process type on the Return Process record determines how receiving, shipping, and serial number tracking is handled.
Advanced replacement is used when you want to ship your customer a usable unit before receiving an unusable unit from your customer. You can then repair or dispose of the unusable unit. Advanced replacement enables you to ship a unit before the unusable unit is received.
The unit you send has a different serial number than the unit you receive and you generally charge a flat rate.
Swap is used when you want to receive an unusable unit from your customer and then ship a replacement, usable unit to your customer.
The unit you send has a different serial number than the unit you receive and you generally charge a flat rate.
Repair and return is used when you want to receive an unusable unit from your customer, repair it, and return the repaired, usable unit to your customer.
The unit you send has the same serial number as the unit you receive and you generally charge time and materials although some repairs may be a flat rate.
Swap is used when you want to receive an unusable unit from your customer and then ship a replacement, usable unit to your customer.
The unit you send has a different serial number than the unit you receive and you generally charge a flat rate.
Repair and return is used when you want to receive an unusable unit from your customer, repair it, and return the repaired, usable unit to your customer.
The unit you send has the same serial number as the unit you receive and you generally charge time and materials although some repairs may be a flat rate.
The following special return types are also used:
- Receive‐only is used when you want to receive a unit from your customer, for example receiving spare parts to put pack in your inventory and credit the customer, or returning exchanged items from a field service repair.
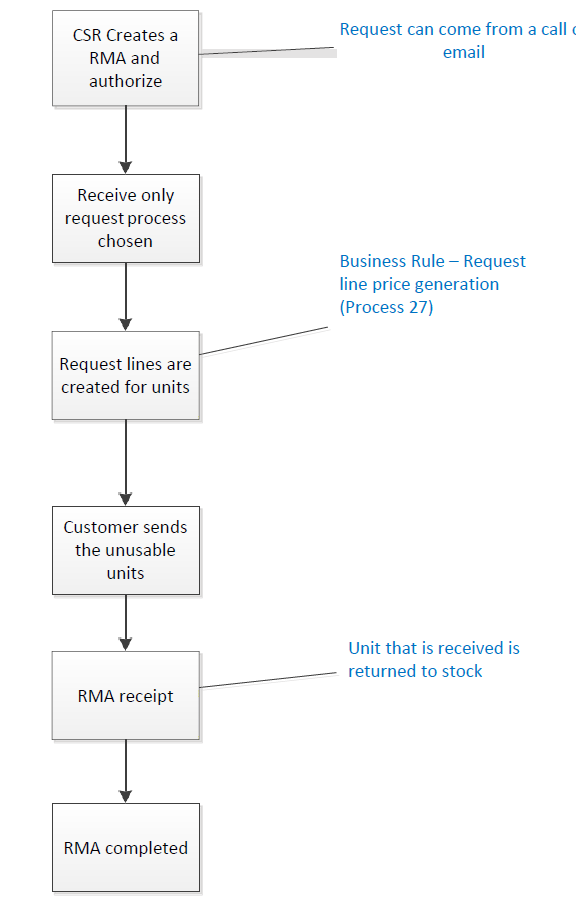
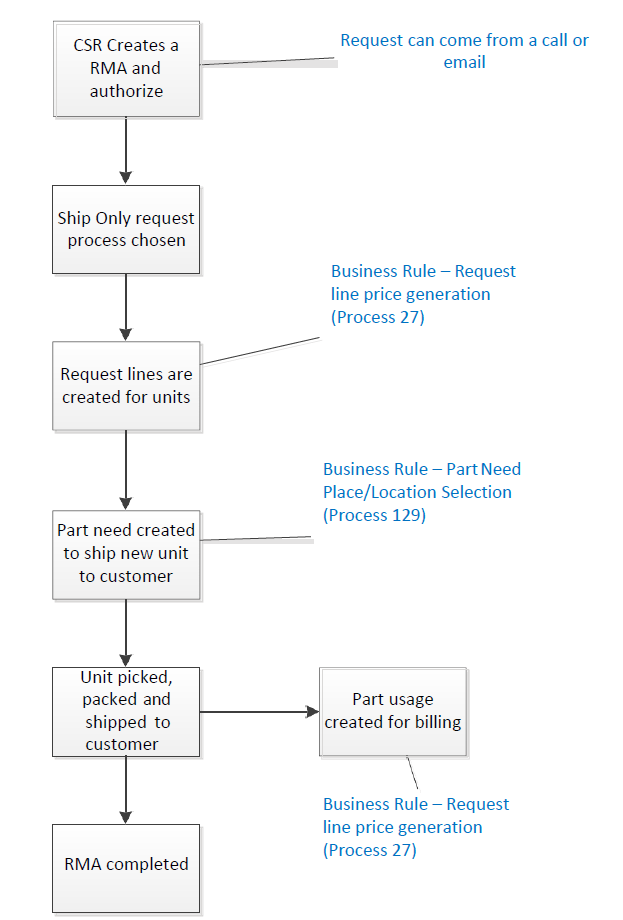
- Ship‐only is used when you want to send a unit to your customer, for example selling a spare part from your inventory and charging the customer.
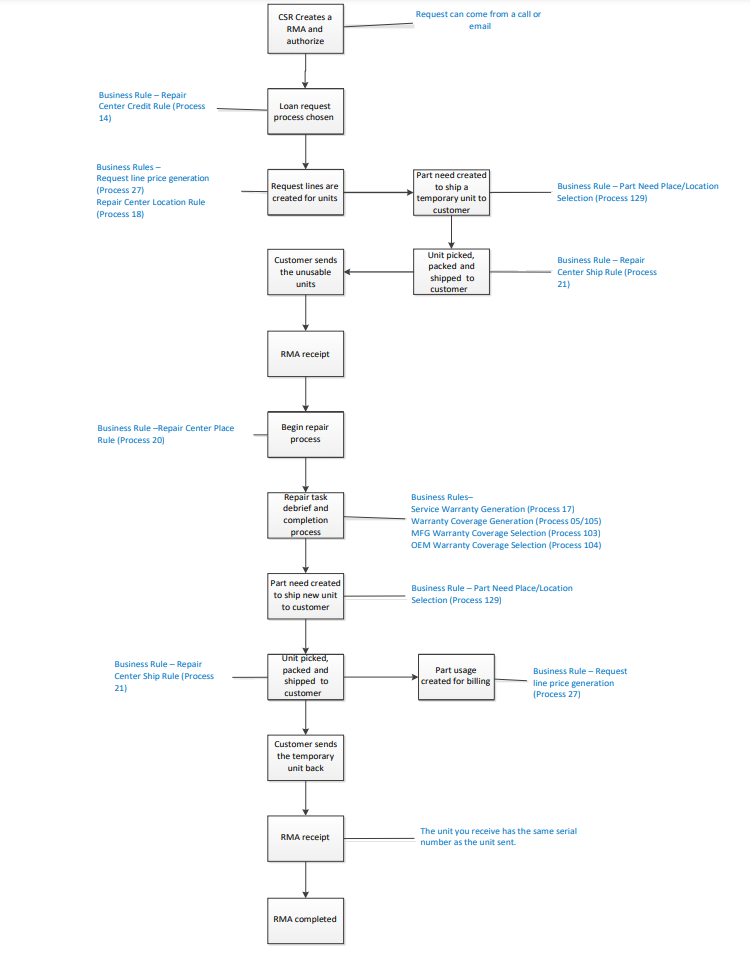
- Loan is used when you want to temporarily send a unit to your customer, for example while you repair the customer’s unusable unit. The unit you receive has the same serial number as the unit you sent.
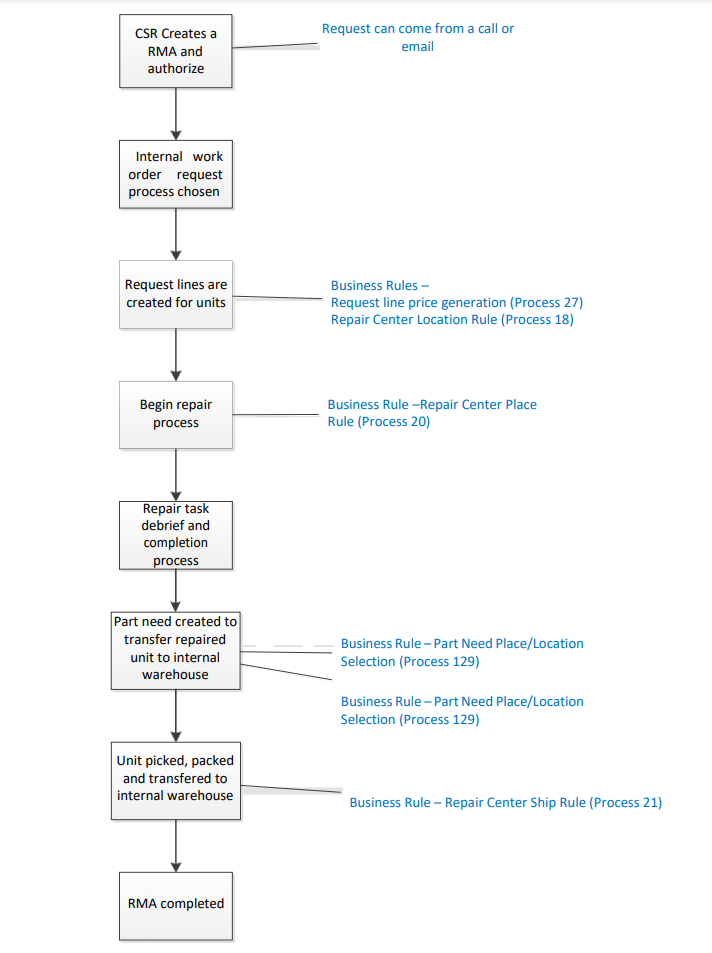
- Internal work order is used when you want to authorize and repair units in stock but are not shipping or receiving them.
 .
.
Billing for Returns
When business rules are set up and the allow‐invoice indicator is set, usage is created for billing when a usable unit is shipped to the customer. You can also enter other time and materials. The price type assigned to the usage determines when it is billed. A price type of “repair” or “misc” is billed when the unit is shipped to the customer. A price type of “credit” is billed when units are received, for example on an advanced replacement.
Return Process Details
For each process, when all units on a line are shipped or received, that line’s status automatically changes to complete. When all lines on an RMA are complete, the status of the RMA is changed to complete.
Advance Replacement
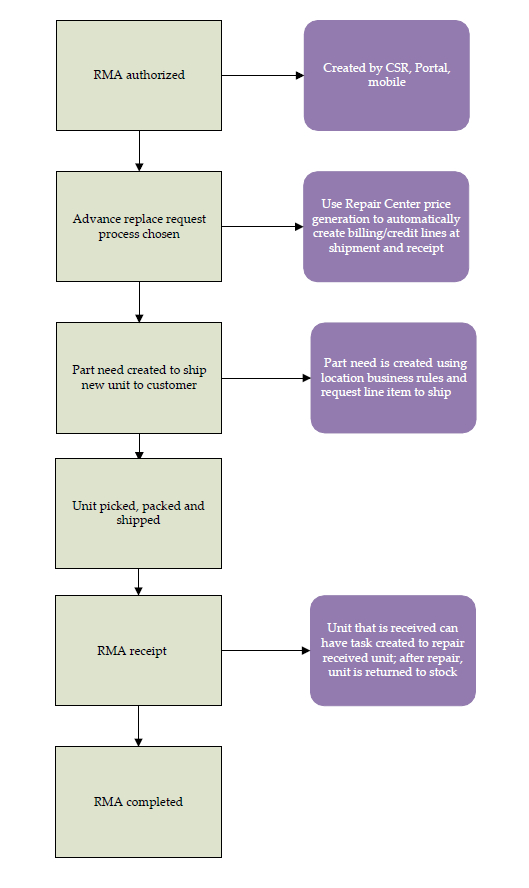
- A call is received from the customer and units are authorized.
- An RMA is created with the appropriate customer information.
- Request lines are created for each type of unit.
- If the units have known serial numbers, they are entered for each unit.
- Usable units are shipped to the customer.
- Part needs are automatically added to the RMA for shipping units to the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the part needs are picked.
- Using the shipment created from picking, the units are shipped to the customer.
- Based on business rules, usage is created for billing.
- Unusable units are received from the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the units are received.
- Based on business rules, usage is created for credit.
Swap
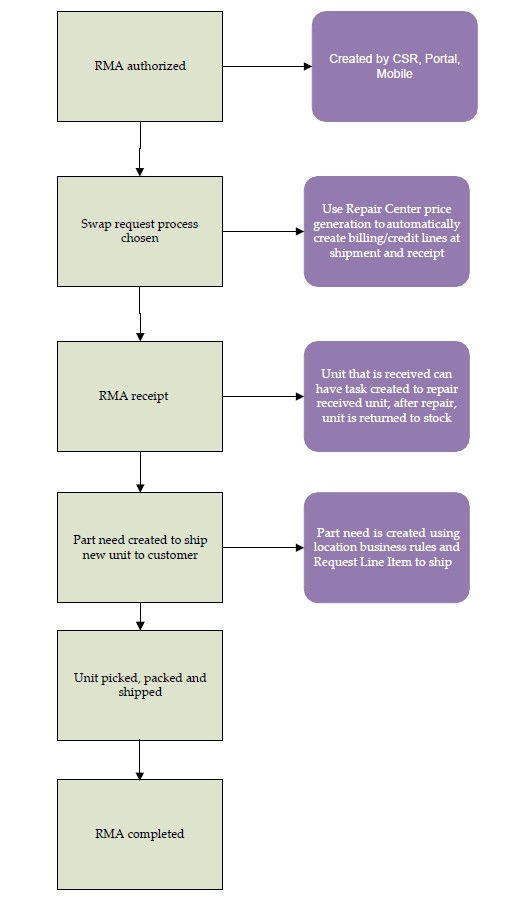
- A call is received from the customer and units are authorized.
- An RMA is created with the appropriate customer information.
- Request lines are created for each type of unit.
- If the units have known serial numbers, they are entered for each unit.
- Unusable units are received from the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the units are received.
- Based on business rules, usage is created for credit.
- Usable units are shipped to the customer.
- Part needs are automatically added to the RMA for shipping units to the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the part needs are picked.
- Using the shipment created from picking, the units are shipped to the customer.
- Based on business rules, usage is created for billing.
Repair and Return
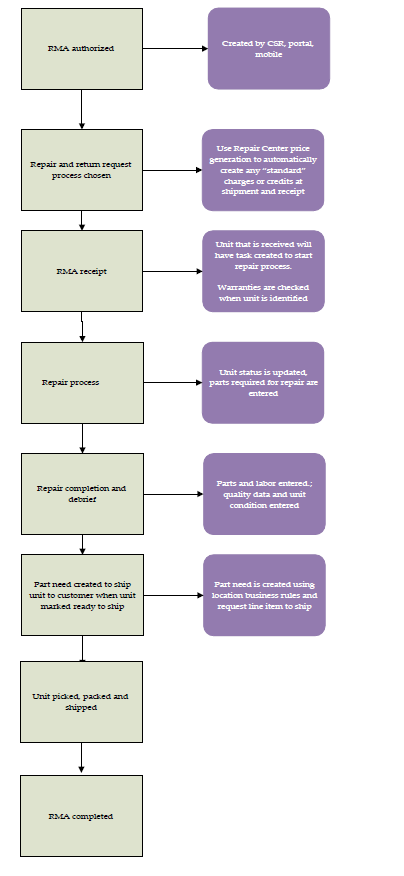
- A call is received from the customer and units are authorized.
- Request lines are created for each type of unit.
- If the units have known serial numbers, they are entered for each unit.
- Unusable units are received from the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the units are received.
- Units are repaired.
- The units are transferred to the bench and repaired. For more information, see “Repair Task Debrief and Completion”.
- Units are transferred to the shipping location.
- Usable units are shipped to the customer.
- When the unit is marked ready to ship, part needs are added to the RMA for shipping units to the customer.
- Using the RMA as a reference, the part needs are picked.
- Using the shipment created from picking, the units are shipped to the customer.
- Based on business rules, usage is created for billing.